Process Selection
Refers to deciding on the way production of goods or
services will be organized
- Occurs as a matter of course when new products or services are being planned, also occurs periodically due to technological changes in products or equipment as well as competitive pressures.
- Has major implications for capacity planning, layout of facilities, equipment, & design of work systems.
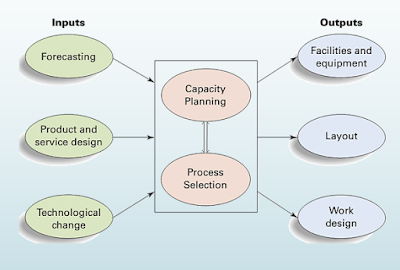
Process selection & capacity planning influence
system design
Process Types
Five basic process types are
- Job shop
- Batch
- Repetitive
- Continuous
- Project
Product or Service & Flexibility Variety & Equipment Flexibility
Job Shop
- Customized goods or services
- Intermittent
- Operates on a relatively small scale
- High-variety goods or services
- Skill level of workers need to be high
Batch
- Moderate volume of goods or services
- Moderate variety
- Not much flexible but Intermittent
- Easy to add or change products or services
Repetitive/Mass
- Higher volumes of more standardized goods or services
- Slight flexibility of equipment
- Skill of workers is generally low
- Sometimes referred to as assembly
Continuous
- High volume of no discrete, highly standardized
- lmost no variety in output
- No need for equipment flexibility
- Skill requirements can range from low to high
Project
A no repetitive set of activities directed toward a unique
goal within a limited time frame
- Used for work that is no routine
- Unique set of objectives to be accomplished in a limited time frame
Such as consulting, making a motion picture, launching a new
product or service etc.
Process strategy
- The importance of flexibility as a competitive strategy is high
- However, flexibility does not always offer the best choice in processing decisions
- Flexible systems & equipment are often more expensive & not as efficient as less flexible alternatives
- In certain instances, flexibility is unnecessary because products are in mature stages, requiring few design changes, & there is a steady volume of output
Flexibility should be adopted with great care; its
applications should be matched with situations in which a need for flexibility
clearly exists.





No comments:
Post a Comment