Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
Integration of financial, manufacturing & human resource
on a single computer system
- ERP software provides a system to capture & make data available in real time to decision makers & other users throughout an organization
- Provides a set of tools for planning & monitoring various business processes
Benefits of ERP
- Show absolute visibility of what is happening in the business
- Make all parts of business more efficient by forcing business-process-based changes
- Better ‘sense of control’ of operations
- Able to integrate entire supply chain including supplier & customer
- Enables far more sophisticated communication with customers, suppliers & other business partners, often giving more accurate & timely information
Implementation of ERP
- Initiation
– Develop business case, project scope & implementation strategy
- Planning
– Establish implementation team, determine goals & objectives, establish metrics
- Analysis & process design
– Analyze & improve current processes, map new processes to be adopted by the system
- Realization
– Install a base system, customization & test the system
- Transition
– Replace the formal system with the new system, data conversion
- Operation
– Monitor & improve system performance, provide continued training & technical support
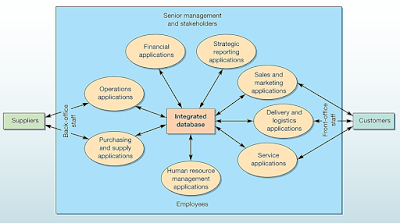
ERP integrates information from all parts of the organization
Major Challenges to ERP Implementation
- Limitations of ERP technical capabilities
- Inconsistency with existing business processes
- Costs
- Implementation (hardware, software, training, consulting) & maintenance
- Impact on organizational structure (front office vs. back office, product line, etc.)
- Changes in employee responsibilities
- Flexibility of software system upgrades
- Implementation timelines
- Availability of internal technical knowledge & resources
- Education & training
- Implementation strategy & execution
- Resistance to change

No comments:
Post a Comment