This blog is created to share knowledge on modern manufacturing systems.
Thursday, September 28, 2017
Inventory planning & control, Types of inventory, Objectives of Inventory Control, Requirements for effective inventory management, Counting Systems,Inventory Costs, Economic order quantity (EOQ)
Inventory planning & control
A stock or store of goods
- The stored accumulation of material resources in a transformation system
- Allow the flexibility
- Exceptional quality
- Give a level of dependability
- Better return on investment (ROI)
Functions of Inventory
- To meet anticipated customer demand
- To smooth production requirements
- To protect against stock outs & take advantage of order cycles
- To hedge against price increases
- To permit operations
- To take advantage of quantity discounts
Enterprise resource planning (ERP), Implementation of ERP, Major Challenges to ERP Implementation
Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
Integration of financial, manufacturing & human resource
on a single computer system
- ERP software provides a system to capture & make data available in real time to decision makers & other users throughout an organization
- Provides a set of tools for planning & monitoring various business processes
Material requirements planning (MRP), Requirements of MRP, MRP input, MRP processing, MRP outputs, MRP II (Manufacturing Resources Planning)
Material requirements planning (MRP)
A computer-based information system that translate
requirements of MPS for end items into time-phased requirements for
subassemblies, components, & raw materials
- Working backward from the due date using lead times & other information to determine when & how much to order
Capacity planning & control, Steps in Capacity Planning, Measuring demand & capacity, Yield management
Capacity management
Capacity: The upper limit or ceiling on the load that
an operating unit can handle.
-The maximum level of value-added activity over a period of time that the process can achieve under normal operating conditions
- Capacity decisions have a real impact on the ability of the organization to meet future demands for products & services
- Capacity decisions affect operating costs
- Capacity is usually a major determinant of initial cost
- Capacity decisions often involve long-term commitment of resources
- Capacity decisions can affect competitiveness
- Capacity affects the ease of management
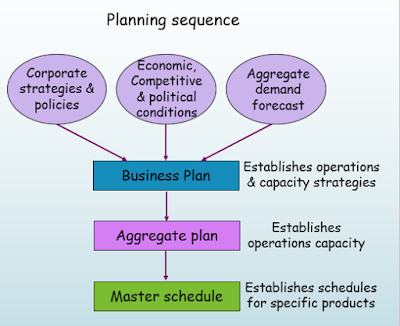
Planning & controlling capacity
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)