Problem Solving
Basic steps in problem solving
- Step 1: Define the problem & establish an improvement goal
- Step 2: Develop performance measures & collect data (check sheet, scatter diagram, histogram, run chart, & control chart)
- Step 3: Analyze the problem (Pareto chart, cause-and-effect diagram)
- Step 4: Generate potential solutions (brainstorming, interviewing, surveying)
- Step 5: Choose a solution
- Identify the criteria for choosing a solution & select the best one
- Step 6: Implement the solution
- Keep everyone informed
- Step 7 : Monitor the solution to see if it accomplishes the goal.
If not, modify the solution, or return to Step 1
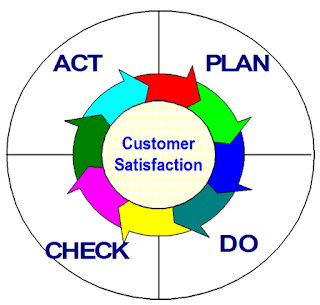
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle
A framework for problem solving & improvement
activities, also referred to as either the Shewhart cycle or the Deming wheel
There are four basic steps in the cycle
- Plan: Begin by studying & documenting current process then collect data. Analyze data & develop a plan for improvement. Specify measures for evaluating the plan.
- Do: Implement the plan, on a small scale if possible. Document any changes made during this phase. Collect data systematically for evaluation.
- Check: Evaluate the data collection during the do phase. Check how closely the results match the original goals of the plan phase.
- Act: If the results are successful, standardize the new method.
- Communicate the new method to all people associated with the process.
- Implement training for the new method.
- If the results are unsuccessful, revise the plan & repeat the process or finish this project.
No comments:
Post a Comment